104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Leetcode
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
題目
Given the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
A binary tree's maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Example 1:
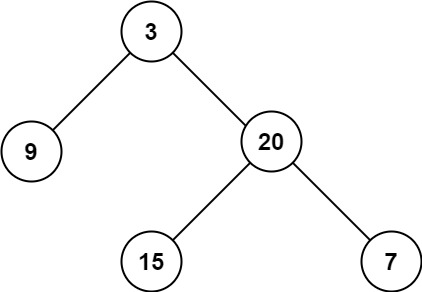
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 3Example 2:
Input: root = [1,null,2]
Output: 2解答
方法一
Recursion (DFS)
Runtime: 80 ms, faster than 73.62% of JavaScript online submissions for Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.
Memory Usage: 47.3 MB, less than 5.07% of JavaScript online submissions for Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.
方法二
Recursion (DFS)
比較左右兩邊子樹的高度,取其最高再加上本身的高度 1
Runtime: 91 ms, faster than 57.09% of JavaScript online submissions for Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.
Memory Usage: 44.8 MB, less than 83.64% of JavaScript online submissions for Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.
方法三
Recursion (DFS) - 尾遞歸
方法二的優化
Runtime: 72 ms, faster than 86.13% of JavaScript online submissions for Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.
Memory Usage: 45.1 MB, less than 68.36% of JavaScript online submissions for Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.
方法四
Iteration (DFS)
Runtime: 76 ms, faster than 78.84% of JavaScript online submissions for Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.
Memory Usage: 46.8 MB, less than 5.07% of JavaScript online submissions for Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.
方法五
Iteration (BFS)
Runtime: 84 ms, faster than 68.47% of JavaScript online submissions for Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.
Memory Usage: 46.6 MB, less than 5.49% of JavaScript online submissions for Maximum Depth of Binary Tree.
Last updated