111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Leetcode
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/
題目
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
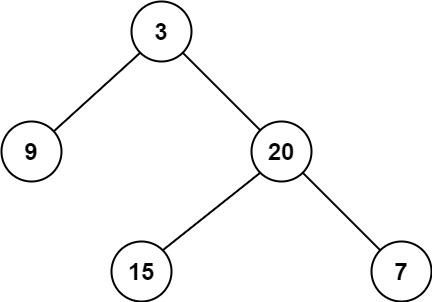
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 2Example 2:
Input: root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Output: 5解答
方法一
Recursion
Runtime: 344 ms, faster than 32.13% of JavaScript online submissions for Minimum Depth of Binary Tree.
Memory Usage: 99 MB, less than 38.19% of JavaScript online submissions for Minimum Depth of Binary Tree.
方法二
Recursion (DFS)
Runtime: 248 ms, faster than 80.42% of JavaScript online submissions for Minimum Depth of Binary Tree.
Memory Usage: 82.2 MB, less than 97.21% of JavaScript online submissions for Minimum Depth of Binary Tree.
方法三
Iteration (DFS)
利用 stack 先進後出的特性達到 DFS 遍歷
Runtime: 278 ms, faster than 66.33% of JavaScript online submissions for Minimum Depth of Binary Tree.
Memory Usage: 99.1 MB, less than 34.14% of JavaScript online submissions for Minimum Depth of Binary Tree.
方法四
Iteration (BFS)
將方法三的 stack 改為 queue 實現,即為 BFS 遍歷
BFS 遍歷的話就不用再儲存最小的 depth,因為會一層一層 level 找,所以找到葉子節點時即可以返回當下 depth 值
Runtime: 321 ms, faster than 43.93% of JavaScript online submissions for Minimum Depth of Binary Tree.
Memory Usage: 99.1 MB, less than 34.14% of JavaScript online submissions for Minimum Depth of Binary Tree.
Last updated